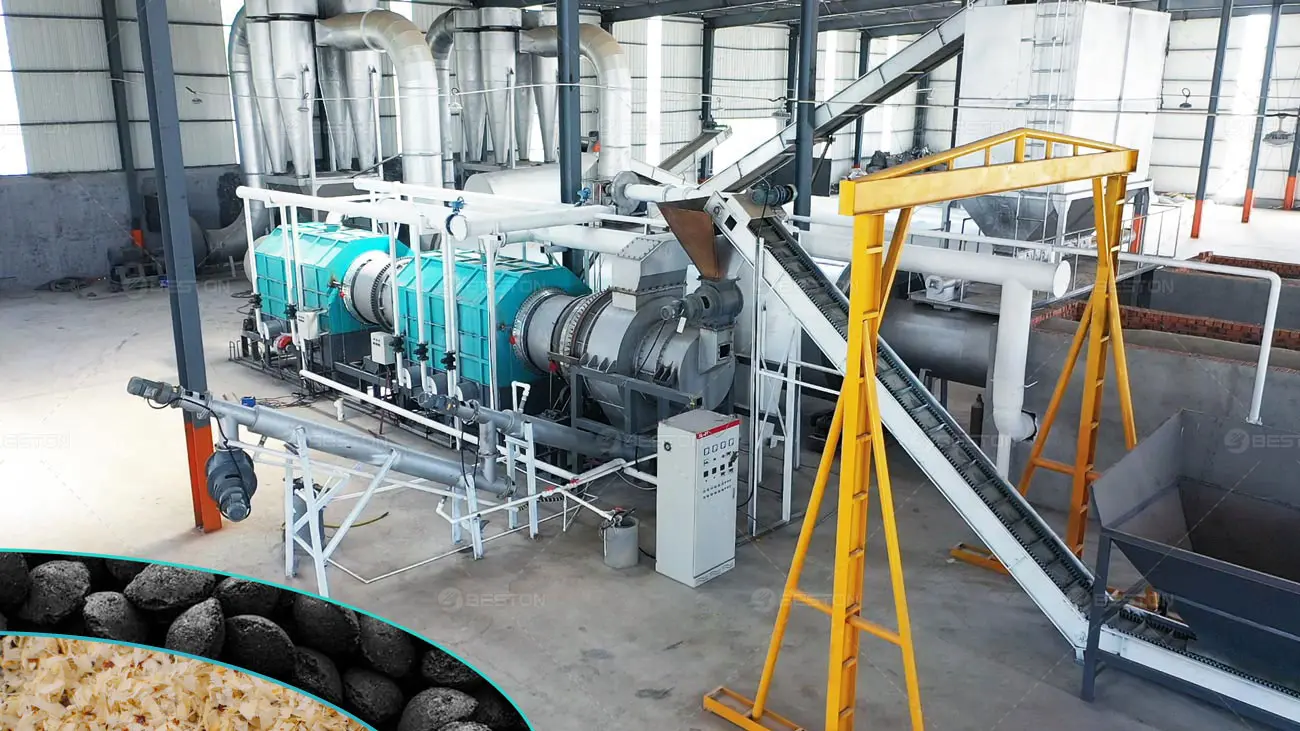
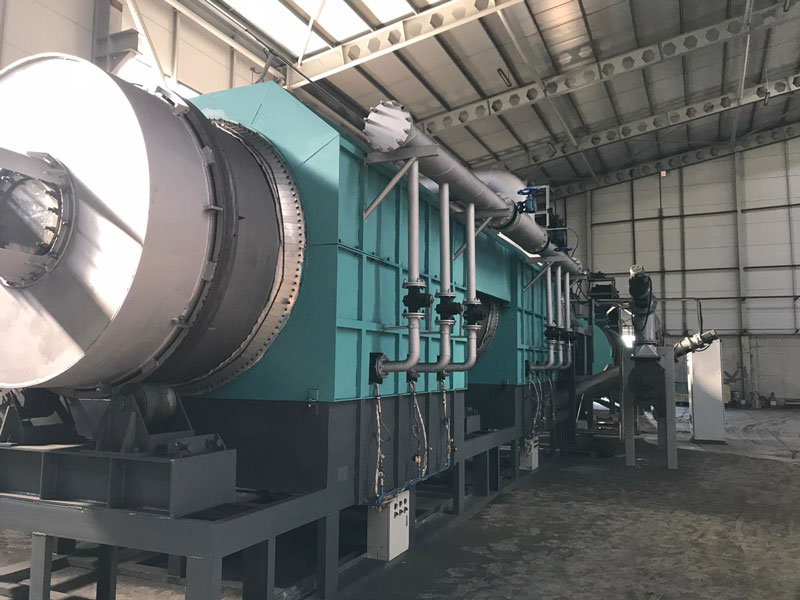
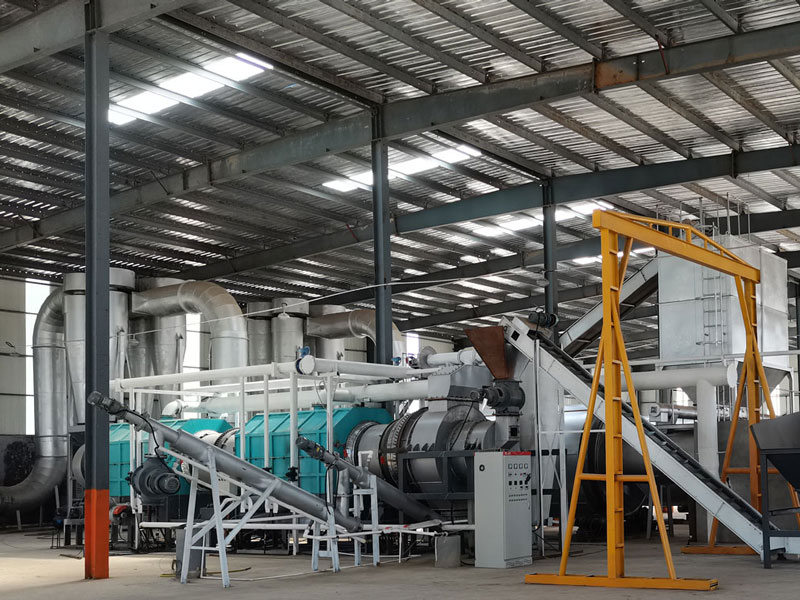
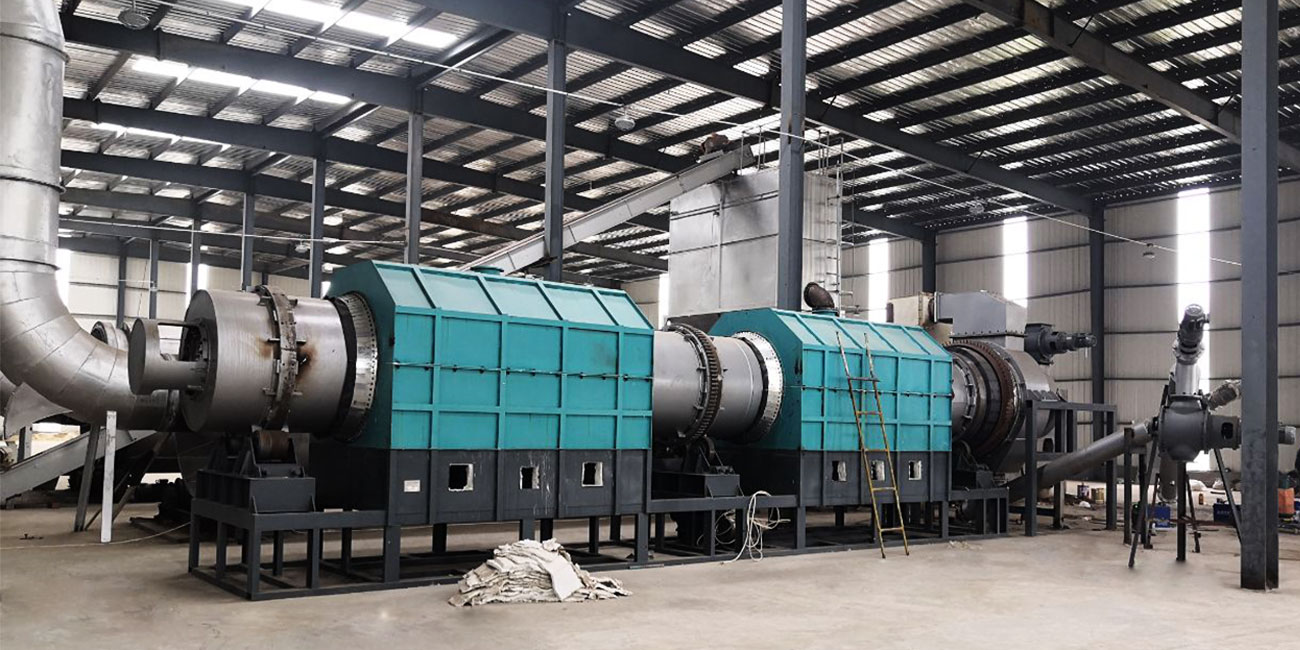
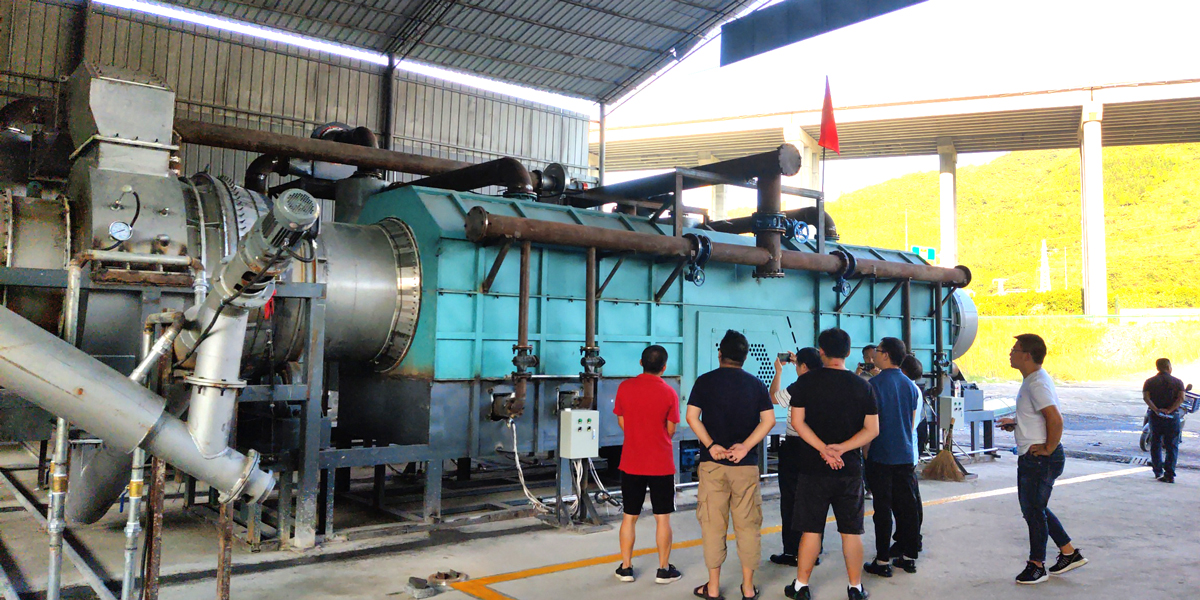
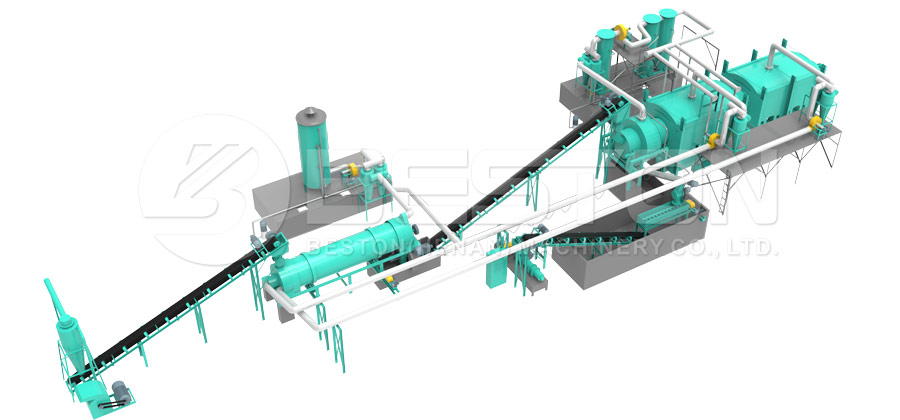
Rural regions often face structural challenges such as limited industrial activity, constrained income channels, and underutilized biomass residues. Deploying modern carbonization equipment provides a practical pathway to convert local waste streams into marketable resources. A charcoal maker helps communities transform low-value materials into stable carbon products that can be sold, stored, or reintegrated into agricultural systems.
Expanding Local Value Creation Through Biomass Conversion
The integration of a biochar machine into rural production chains enables the systematic conversion of agricultural residues into durable carbon materials. Crop waste, forestry byproducts, and municipal green waste become feedstocks for localized economic activity instead of burdens on landfills. The equipment produces a clean-burning fuel and a soil-enhancing amendment. These outputs support downstream industries, stimulate small-scale trade, and create dependable revenue channels for villages that previously relied heavily on seasonal farming income.
Enhancing Resource Efficiency and Reducing Waste Disposal Costs
Rural zones often lack advanced waste collection and processing systems. A pyrolysis machine for biochar addresses this deficiency by compressing the biomass burden into higher-value commodities. Controlled thermal decomposition stabilizes the carbon content and eliminates open burning practices that contribute to airborne pollutants. The shift toward systematic biomass management reduces waste-handling expenses and minimizes environmental degradation. Communities experience notable improvements in air quality, land cleanliness, and overall ecological stewardship.

Strengthening Rural Employment and Technical Skill Development
Introducing a biomass pyrolysis plant into a village environment generates employment opportunities across several operational categories. Feedstock preparation, equipment operation, carbon product packaging, and local marketing all require labor inputs. Workers acquire technical competencies related to process monitoring, thermal control, and materials handling. These skills enhance their future employability and help diversify the rural workforce. The presence of such equipment catalyzes auxiliary services as well, including logistics, maintenance, and equipment servicing networks.

Supporting Agricultural Productivity Through Biochar Utilization
The carbonized output from a charcoal maker provides agricultural benefits that are particularly valuable in regions with depleted or erosion-prone soils. Biochar enhances soil cation exchange capacity, moisture retention, and microbial habitat stability. Farmers using biochar experience improved fertilizer efficiency and greater crop resilience. Higher yields reinforce household incomes and create a reinforcing cycle between biomass processing and agricultural prosperity. This synergy elevates both economic and environmental stability.
Encouraging Small-Scale Entrepreneurship and Market Diversification
Rural entrepreneurs can leverage a biochar machine to produce fuel briquettes, soil enhancers, carbon-based additives, and specialty carbon products for local industries. Market diversification reduces reliance on a single commodity and opens channels to urban markets seeking cleaner-burning alternatives. Small workshops often emerge around a biomass pyrolysis plant, generating a cluster effect that magnifies economic output. As product portfolios expand, rural communities gain bargaining power, better price stability, and improved financial resilience.
Promoting Long-Term Rural Sustainability
A pyrolysis machine for biochar supports long-term rural sustainability by converting waste into assets, advancing circular resource use, and reducing environmental pressures. Its deployment aligns with global renewable energy policies and carbon management initiatives. Communities adopting this technology develop a more diversified and shock-resistant economy. The combination of new income streams, enhanced environmental quality, and improved agricultural performance contributes to durable rural development grounded in efficient biomass utilization.